A few decades ago, you might have noticed solar panels when driving through rural areas on a radio tower, or perhaps you’d seen them in use at a scientific research facility or on images of the international space station.
These days, it seems like solar panels are popping up everywhere, with many modern homeowners opting to trade in their expensive and inefficient electricity bills for clean, environmentally conscientious solar energy that requires virtually no maintenance and significantly cuts costs over time. From backyard barbeques to complete electric power replacement, modern homes — and offices for that matter — are quickly adapting to the modern solar power trend.
But it’s not just homes that are benefiting from the energy-producing rays of the sun. There is a wide variety of solar gadgets emerging on the modern market, from the ingenious to the entertaining.
There are a great number of portable devices that both businesspeople and vacationers alike depend on for work, play, and communication, the foremost of which is perhaps the laptop. Most laptop owners are familiar with a common frustration associated with their use; while the laptop is certainly portable, it only functions a short while away from its electric energy source. Solar power comes into play for laptop owners with newly-developed laptop battery chargers; imagine getting extra hours of computation, correspondence, or even game playing out of your machine by harnessing the natural energy of the sun.
For those who like to listen to their music out of doors, many audio equipment companies now offer solar-powered headsets, which can provide excellent quality radio, cd, or mp3 tunes without the expense or hassle of batteries; these inventive devices give ‘fun in the sun’ a whole new meaning.
In the garden, solar panels are a great way to provide illumination at night; solar “spotlights” or path lights can be placed throughout the natural landscape without the need for a clutter of wires and cables, and can give your garden a gorgeous night view or help guide your way from the garage once the sun’s gone down.
The increasingly popular use of amphorous solar cells, which are flexible unlike conventional models, are resulting in an array of important applications such as camping gear (some tents feature solar-paneled surfaces), clothing, and more.
With applications from the small and amusing to the truly immense, solar panels are proving an important element of modern energy production. Make this clean and cost-efficient power source a part of your life, and find a solar gadget to delight you and deliver you from electric dependency.
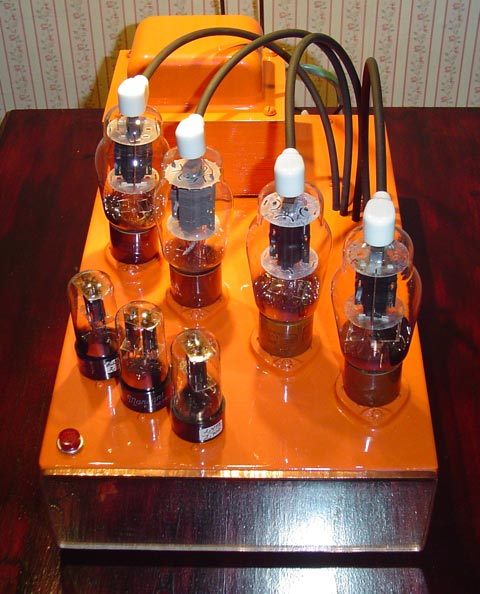
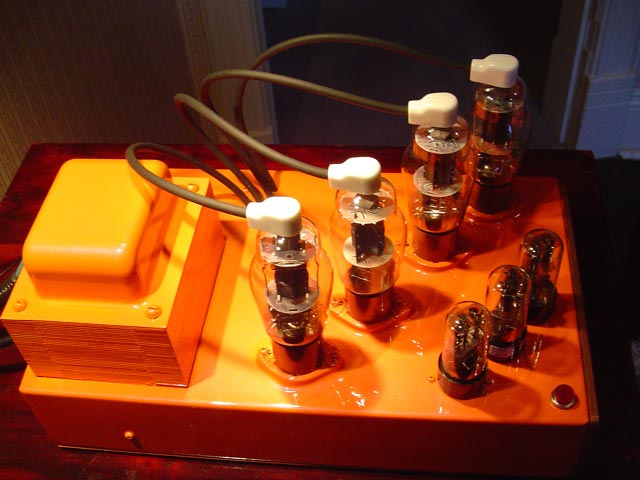
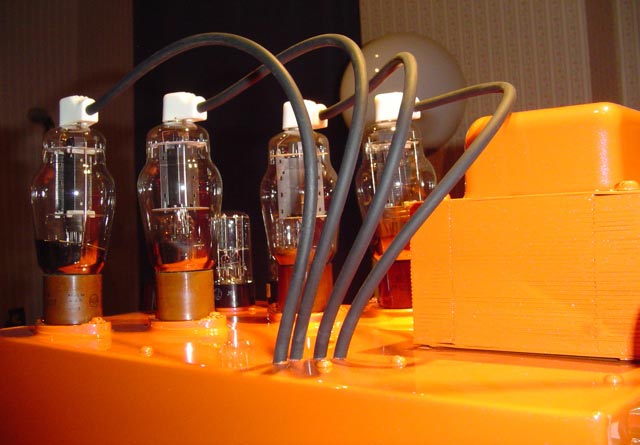






 lot of study was done in the field and the initial operational amplifiers, based on vacuum tubes, were a result of the research done in Bell labs. By 1960’s, vacuum tube op amps had given way to solid state devices and hybrid operational amplifiers were entering the scene.
lot of study was done in the field and the initial operational amplifiers, based on vacuum tubes, were a result of the research done in Bell labs. By 1960’s, vacuum tube op amps had given way to solid state devices and hybrid operational amplifiers were entering the scene. Here are some other uses:
Here are some other uses: